Uterine Fibroid Treatment
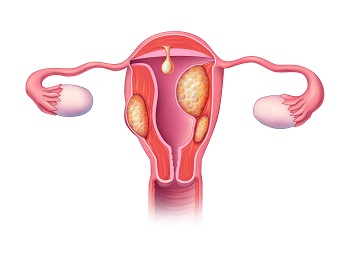
Uterine Fibroids (Leiomyoma)
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that originate from the uterine muscle tissue. Fibroid growth is dependent on estrogen and progesterone and is rare before puberty. Fibroid growth increases in prevalence during the reproductive years and often decreases in size after menopause. Uterine fibroids can alter a woman’s period and cause a variety of bulk pelvic symptoms.
Fibroids are found in approximately 70 percent of white women and in about 80 percent of African American women in the United States by the time they are 50 years old. Fibroids are benign and do not spread to other regions of the body. The risk of malignancy for uterine fibroids is very low.

Download our illustrated guide to the diagnosis and treatment of uterine fibroids.
View and Download the InfographicUterine Fibroid Symptoms, Testing and Treatments
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that originate from the uterine muscle tissue. Fibroid growth is dependent on estrogen and progesterone and is rare before puberty. Fibroid growth increases in prevalence during the reproductive years and often decreases in size after menopause. Uterine fibroids can alter a woman’s period and cause a variety of bulk pelvic symptoms.Who does it impact?
Fibroids are found in over 60% of women by the time they are 50 years of age. Fibroids are benign and do not spread to other regions of the body. Most fibroids do not cause any symptoms and the risk of malignancy for uterine fibroids is very low.Symptoms
The symptoms and treatment options depend on the size, number, and location of the tumors. The most common symptom is excessive menstrual bleeding. Fibroids can also often cause bulk symptoms including pelvic pressure, bloating, urinary frequency, back pain, and constipation. • Heavy menstrual bleeding • Pelvic pressure • Bloating sensation • Urinary frequency • Low back pain • ConstipationHow are uterine fibroids diagnosed?
It is important to differentiate between other possible causes of uterine growth and abnormal bleeding. A correct diagnosis will determine the proper treatment for you. Because most women will not exhibit every potential symptom, the diagnosis is usually confirmed by pelvic ultrasound or MRI. Imaging helps determine appropriate treatment options. Ultrasound uses sound waves to get a picture of your uterus to confirm the diagnosis. The technician places the ultrasound device (transducer) over your abdomen, or inside the vaginal canal to get images of your uterus. Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is a noninvasive test that uses a powerful magnet to view the size and location of fibroids and exclude other types of disorders.Treatment Options
Hysterectomy, or surgical removal of the uterus, provides a definitive cure for women with symptomatic fibroids who do not wish to preserve fertility. Hysterectomy can be performed through an abdominal incision or using a less invasive approach with laparoscopic assistance. Recovery ranges from 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the procedure. Myomectomy is the preferred surgical procedure for women with submucosal fibroids who wish to preserve their uterus or fertility. This procedure consists of surgically removing the fibroid from the uterus while leaving the uterus intact. Recovery from this procedure is slightly less than that of a hysterectomy. Hormone therapy can be used to temporarily relieve heavy menstrual bleeding and menstrual pain. These treatments can also shrink fibroids but can’t make them disappear completely. Hormones are usually only used for a limited time because of the risk of side effects. Fibroids may regrow once hormonal therapy is stopped. Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) is an effective minimally invasive alternative to hysterectomy and in select cases, myomectomy. UFE is performed under imaging guidance with intravenous conscious sedation. An interventional radiologist guides a very thin catheter, about the size of a strand of spaghetti, into the specific arteries supplying blood to the fibroid. The doctor then releases small particles into the targeted arteries which causes the fibroid to shrink.Post Treatment
Following UFE, some women may experience discomfort relating to post-embolization syndrome, including pelvic pain, cramping, nausea, low-grade fever, fatigue and discomfort. These symptoms generally resolve with conservative treatment within 2–7 days. Depending on the location and size of the treated fibroid, some women may also experience some vaginal discharge for 1–2 weeks after the procedure.IVC Can Help
At IVC® we specialize in Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) which targets the abnormal blood supply to the fibroid, causing the fibroid to shrink. UFE avoids surgery and can preserve your uterus, control symptoms, while improving quality of life. Approximately 9 out of 10 women who undergo uterine fibroid embolization will experience significant symptomatic improvement. Patients are generally able to resume most daily activities within 1 to 2 days after the procedure.Telehealth Appointments are Available!
Online appointments offer another option for patients who are practicing social distancing or otherwise find it difficult to be seen in the office. Using a smartphone or computer, you may connect securely and privately with one of our providers. • Secure and private • HIPAA compliant Visit https://www.ivein.com/telehealth to schedule an appointment. At IVC® we are dedicated to helping our patients live their best lives. Contact us today. Call 801.379.6700 Learn more at ivein.comResources
https://www.ivein.com/conditions/uterine-fibroids/

Symptoms
The symptoms and treatment options depend on the size, number, and location of the tumors. The most common symptom is excessive menstrual bleeding. Uterine fibroids often also cause bulk symptoms which include pelvic pressure, bloating sensation, urinary frequency and urgency, low back pain, and constipation.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pressure
- Bloating sensation
- Urinary frequency and urgency
- Low back pain
- Constipation

Testing for Uterine Fibroids
It is important to differentiate between other possible causes of uterine growth and abnormal bleeding. A correct diagnosis will determine the proper treatment for you. Other causes of uterine growth and abnormal menstrual bleeding include:
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial polyps
- Uterine malignancy
Because most women will not exhibit every potential symptom, the diagnosis is usually confirmed by using imaging of the pelvis, with transvaginal ultrasound or MRI.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to get a picture of your uterus to confirm the diagnosis of uterine fibroids. The technician places the ultrasound device (transducer) over your abdomen (transabdominal) or in some cases inside the vaginal canal (transvaginal) to get images of your uterus.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is a non-invasive test that uses a powerful magnet to view size and location of uterine fibroids, exclude other types of tumors, and help to determine appropriate treatment options. The MRI requires the administration of an intravenous contrast agent, and requires the patient to lay flat and very still for about 45 minutes to complete the exam.
Treatment of Uterine Fibroids
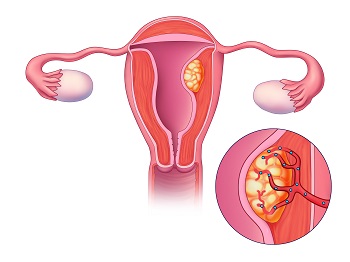
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
Uterine fibroid embolization, or UFE, is a minimally-invasive treatment that targets the abnormal fibroid blood supply which causes the fibroid to shrink. UFE avoids surgery, can preserve your uterus, control symptoms, and improves quality of life. Approximately 9 out of 10 women who undergo uterine fibroid embolization will experience significant symptomatic improvement.
Under X-ray guidance and sedation, an interventional radiologist guides a very thin catheter, about the size of a strand of spaghetti, into the specific arteries supplying blood to the fibroid. Once the catheter is in the proper position, the doctor releases small particles into the targeted arteries which causes the fibroid to shrink. When the uterine fibroid embolization is completed, the catheter is removed.
In order to minimize discomfort, patients are given medication before, during and after the procedure to reduce inflammation and help alleviate procedure-related pain. Patients can typically resume most normal daily activities within 24 hours following embolization.
Following UFE, some women may experience discomfort relating to post-embolization syndrome, including pelvic pain, cramping, nausea, low-grade fever, fatigue and discomfort. These symptoms generally resolve within 2-7 days.
Depending on the location and size of the fibroid some women may also have some vaginal discharge for 1-2 weeks after the procedure. This occurs because the tissue of the fibroid is dying and may slough off into the endometrial cavity.