Compression Fractures
Compression fracture typically occur in the setting of underlying osteoporosis which weakens bone structure. Compression fractures may be secondary to a notable traumatic event such as a fall, but may also occur even something as simple as sneezing. Some patients may not be able to identify an exact time when the fracture occurred.
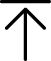
The spine is made up of many vertebral bodies stacked on top of each other. Muscles and ligaments attach to the vertebrae to provide stability and facilitate movement. Compression fractures may cause significant vertebral body deformity and loss of height. It is also possible that pieces of the bone may also project backwards into the spinal canal causing compression on the spinal cord and critical nerves.
Vertebral bodies typically become weaker with age due osteoporosis. Healthy vertebrae can also fracture when subject to intense trauma or, less commonly, when a tumor involves the bone. Compression fractures are most often diagnosed in post-menopausal women, though they are not uncommon in older men as well.
Download our illustrated guide to the diagnosis and treatment of vertebral compression fractures.
View and Download the Infographic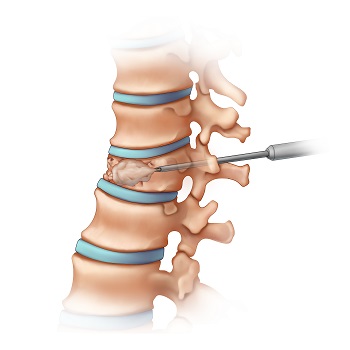
Vertebroplasty
Vertebroplasty is performed using fluoroscopic x-ray guidance. An interventional radiologist guides the treatment needle into the fractured vertebral body and injects bone cement that binds and stabilizes the fracture. The cement stabilizes the bone within a few minutes. After the cement is injected, the physician will remove the needle and a small dressing will be applied over the skin access site.
Advantages of cement augmentation include:
- Short procedural time
- Minimally invasive
- Performed as an outpatient
- Can quickly return to activities as tolerated
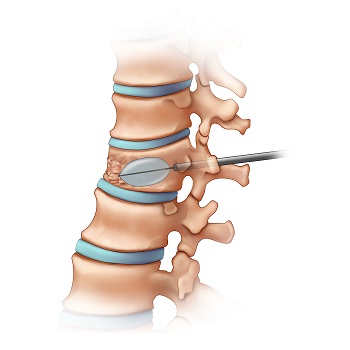
Kyphoplasty
Kyphoplasty is similar to vertebroplasty, but utilizes a balloon or other augmentation device to help contain cement and restore height to a compressed vertebral body. Cement is then used to bind and stabilize the fracture.
Advantages of cement augmentation include:
- Short procedural time
- Minimally invasive
- Performed as an outpatient
- Can quickly return to activities as tolerated